The HackTrack is the official fun side of a Brainhack event, where people can work together on projects.
What projects? Any kind! From exploding brains to resource gathering and data sharing!
Submit Projects
Explore the incredible projects submitted for this year's hackathon.

Poppy & Bagel: How to FAIRly curate, process, and share your neuroimaging datasets
BIDS
Containers
reproducibility
Poppy & Bagel: How to FAIRly curate, process, and share your neuroimaging datasets
Curating data, running reproducible pipelines, creating data dictionaries, integrating data from collaborators, making sensitive data FAIR - these tasks are hard; and we all have to deal with them every day. Here we aim to serve Nipoppy and Neurobagel - a set of protocols and tools with modular framework that one can adopt as needed to simplify common data organization, processing, harmonization, and sharing tasks on neuroimaging datasets.
We cover BIDSification, containerized processing with completion tracking, annotation of phenotypic data, and generation of knowledge graphs for distributed data discovery and sharing.
This is a useful project for those who:
- Feel frustrated replicating work by others or even reproducing your own work from 6 months ago
- Struggle with BIDSification of data
- Spend endless hours trying to match column names in tabular data files
- Work with multi-site datasets
- Support open-science but work with datasets that have privacy issues
- Want to create a community to build a common ecosystem
We have experienced all these issues ourselves in the past, and so we are here to prevent future grief to newcomers!
GitHub issue
Project URL

BIDS 2.0
BIDS
BIDS 2.0
- triage more issues from https://github.com/bids-standard/bids-2-devel/issues : categorize into ToDo, Punted (close), BIDS 3.0
- progress forward on “ToDo” or “In Progress” items of the BIDS 2.0 project: https://github.com/orgs/bids-standard/projects/10, in particular (but not limited to)
- https://github.com/bids-standard/bids-specification/pull/1775
- https://github.com/bids-standard/bids-specification/pull/1809
GitHub issue
Project URL

The BIDS connectivity project - finalization of BEPs
BIDS
Connectivity
Diffusion
EEG
PET
MEG
The BIDS connectivity project - finalization of BEPs
Besides BIDS’ success, expansion, and description of multiple data modalities, gaps still exist in developing the standard to effectively support the process of scientific results reporting. Among others, this prominently refers to data obtained through and during connectivity analyses. This comprises brain parcellations, connectivity maps, structural and functional connections, major white matter tracts, diffusion signal models, white matter tractograms and tractometry, as well as networks based on dimensionality reduction. Sharing processed data and features in addition to raw and minimally processed data is critical to accelerating scientific discovery. This is because substantial effort, software, and hardware instrumentation, and know-how are required to bring raw data to a usable state. The aim of the present project is to extend the BIDS standard to encompass derivatives resulting from experiments related to macroscopic brain connectivity (U.S. National Institutes of Health NIMH R01-MH126699). During the Brainhack, we would like to
- Finalize the existing BEPs (BEP17 - Relationship matrices, BEP38 - Atlases, BEP39 - Dimensionality reduction-based networks)
- Gather feedback from experts, users, tool developers, ie everyone!
- Discuss next steps, e.g. software integrations
GitHub issue
Project URL

NARPS Open Pipelines
fMRI
FSL
GLM
Nipype
SPM
reproducibility
NARPS Open Pipelines
The goal of the NARPS Open Pipelines project is to create a codebase reproducing the 70 pipelines of the NARPS study (Botvinik-Nezer et al., 2020) and share this as an open resource for the community. We base our reproductions on the original descriptions provided by the teams and test the quality of the reproductions by comparing our results with the original results published on NeuroVault.
The Neuroimaging Analysis Replication and Prediction Study (NARPS-Botvinik-Nezer et al., 2020) aimed to provide the first scientific evidence on the variability of results across analysis teams in neuroscience. 70 teams were asked to analyze the same dataset (task-fMRI with 108 participants) and then, to provide their methods and results to be later analyzed and compared.
We would like to focus on these tasks during the Brainhack:
- Start writing the pseudo code of a pipeline based on the knowledge of participants (i.e.: which fMRI analysis software they are used to, whether they use Python or not, …)
- Start reproducing the pipeline from the pseudo code,
- Improving documentation and accessibility of the project.
GitHub issue
Project URL

IDEAS: Interactive data exploration and analytics system
LLM
behavior
IDEAS: Interactive data exploration and analytics system
Develop and use bots+LLMs+agents to query the graph stores, create an analysis strategy to answer the question, and/or search some literature. For a general review/overview of agent-based systems see the figures here: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.02831
GitHub issue
Project URL

Neuroimaging zombies
git
preprocessing
quality control
Neuroimaging zombies
The Neuroimaging zombies projects aims at providing guidelines on how to test whether an effect from the literature is replicable (more than reproducible), and how to prevent our own results to turn into irreplicable effects.
We propose to work on our 3 axes:
- preprocess a public dataset with your favourite tool and upload the results to GIN
- work on reference Quality Control
- work on the reference pipelines for some well established neuroimaging results
Join our Mattermost channel at brainhack.org, and check these slides to learn more about the project at osf.io.
GitHub issue
Project URL
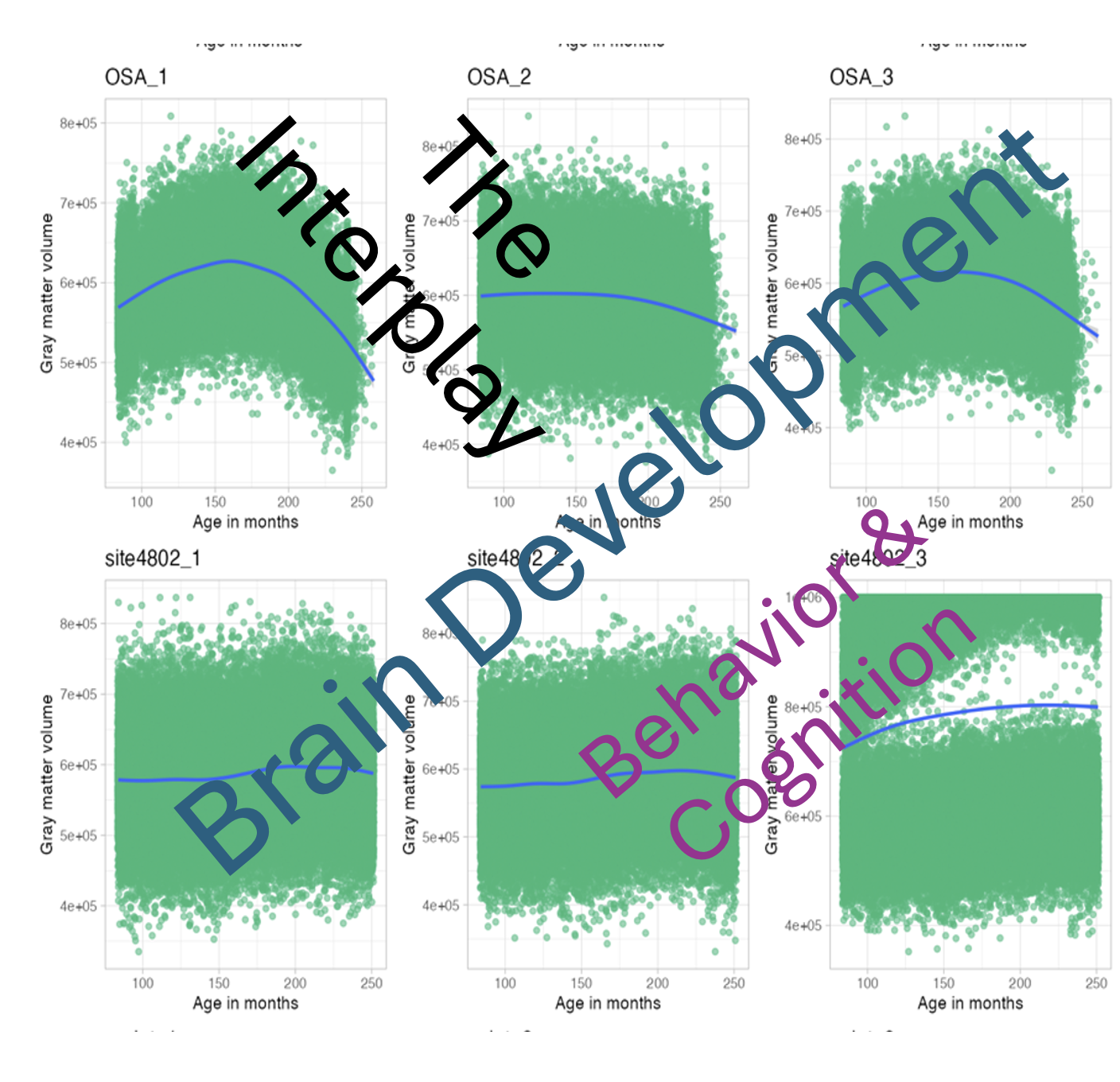
Interplay between Brain Behavior & Cognition
behavior
cognition
Interplay between Brain Behavior & Cognition
As a part of a study to examine the interplay between brain, behavior, and cognition, seven sites internationally have simulated longitudinal datasets of how they envision these interactions to occur. Each site generated three sets of of data, each with 10,000 participants over seven waves, ranging from 7 to 20 years of age. Each site generated these datasets independently and our keeping the key to what they embedded into the data secret. The goal of this brainhack project is to try and determine the hidden developmental treasures hidden within each dataset.
GitHub issue
Project URL

Psy2R - an R package for better inference in multivariate statistical analysis
statistics
documentation
Psy2R - an R package for better inference in multivariate statistical analysis
We consistently use massive datasets across neuroscience and psychology. The routine gathering of big data requires that we are well equipped with tools that allow us to conduct appropriate multivariate statistics. This project aims to produce an R package that allows the researcher to overcome little discussed limitations of traditional multivariate statistical analyses.
Multivariate statistical analysis (e.g. MANOVA and repeated-measures ANOVA) typically follows a two stage procedure; an omnibus test of the global null hypothesis followed by post-hoc tests of specific effects. It is not well known that under certain circumstances, such as when the omnibus test is overpowered, that the type 1 error rate for this procedure is drastically inflated, sometimes to a type 1 error rate of 1! It is even less well known that this procedure can lead to an even lessor known type IV error, which is the incorrect interpretation of a correctly rejected hypothesis. This is caused when the follow-up contrasts are inadequate to test the question of interest, as can occur when testing simple effects.
It is possible to avoid these dragons by using an alternative procedure where all inferences are derived from simultaneous confidence intervals (SCIs) on contrasts of interests. The ‘simultaneous’ bit means that the same statistic contributes to both the omnibus and the contrast tests for significance, which controls the type 1 error rate. Even better, computing confidence intervals on contrasts of interests allows reseachers to move away from binary decision-making (is something significant or not?) to interpretations involving magnitude (how big is this effect likely to be at the population level?).
One piece of software (PSY) can produce SCIs appropriate for both planned analyses (where contrasts are defined independently of the data) and for more flexible analyses where contrasts are defined on a post-hoc basis. However, this software is only available for use on windows and cannot be scripted into reproducible workflows. Our goal is to build an R package that implements the functions of PSY, and to make this method of statistical inference available to the masses!
Our goals for OHBM Brainhack 2024 are:
- Convert some key functions of the Psy source pascal code to R functions: these functions compute the largest contrast effect you could expect to get if the null hypothesis is true, when you have between and within repeated measures.
- Explore the overlap between Psy, emmeans and MBESS, to make sure we recycle where appropriate
- Replicate analyses between the original Psy software and the R implementation
GitHub issue
Project URL

Nilearn: Statistics and Machine Learning for Neuroimaging in Python
nilearn
documentation
statistics
machine learning
Nilearn: Statistics and Machine Learning for Neuroimaging in Python
Nilearn is an open-source Python package for fast and easy analysis and visualization of MRI brain images. It provides statistical and machine-learning tools, with instructive documentation and a friendly community. It includes applications such as multi-voxel pattern analysis (MVPA), decoding, predictive modelling, functional connectivity, and brain parcellations.
Recent work in Nilearn has been centered on developing a new API to allow users to seamlessly work with surface data in a manner similar to volumetric data, enhancing support for the General Linear Model (GLM), enhancing the BIDS interface, and improving and updating the infrastructure and codebase.
We want to dedicate these Brainhack days towards direct interaction with our user-base and resolving any specific issues they might have. To this end, we encourage users to simply pop-in-and-say-hi. They are also welcome to present their queries via neurostars.org or open new issues/PRs on our GitHub repo. In addition, any interested contributors are also encouraged to work on pre-existing issues on our GitHub. To get started, new contributors should look for the “Good First Issue” or “Hackathon” labels.
GitHub issue
Project URL
Reproinventory
documentation
reproducibility
Reproinventory
When planning for a training event for reproducible research, there are many training materials to choose from to teach tools such as git/github, bash, datalad, etc. There are inventories of such training material in some places (ReproRehab, INCF training space, Hitchhicker guide to the brain, etc) but we are lacking i) a set of tags to annotate training material (duration, targeted audience, etc) ii) a place where there can be some crowd curation and annotation of these materials. We propose to develop a set of tags and an inventory of training material for reproducible neuroimaging that can be reused by other resources and be crowd-curated. This project is under the auspices of the INCF-ReproNim train the trainer fellowship.
GitHub issue
Project URL
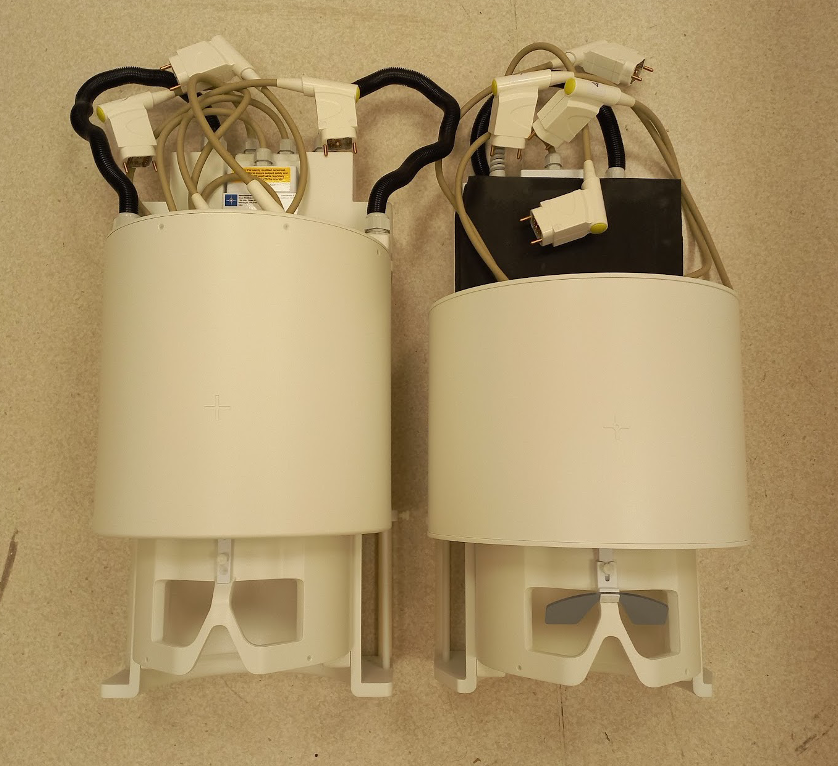

Hack your RF coil
7T
fMRI
quality control
Hack your RF coil
There are more than 100 7T scanners installed around the world and virtually all of them are equipped with an 32ch RF coils from Nova Medical. In the last decade, this coil model has evolved from a niche engineering challenge for prototype scanners to a mainstream FDA-approved medical product. Despite the current abundance of this coil, there are no public quality metrics about it’s stability, consistency across sites, nor across models of single channel transmit (sTx) and multi-channel transmit (pTx).
However, these QA metrics are vital for the upcoming transition of most 7T scanners. Namely, until now almost all 7T scanners were used as single-channel transit systems (e.g. SIEMENS Magentom 7T, classic and Terra). But the new generation of FDA-approved 7T scanners that are solely used as parallel transmit systems (e.g. SIEMENS Terra.X). While the common pTx Nova coil has been successfully validated for a number of clinical imaging protocols, it has never been compared with the sTX coil for highly accelerated fMRI protocols.
Pilot experiments suggest that the pTx coil performs worse in tSNR limited fMRI protocols. This is despite the fact that the transmit performance is improved.
The goals of this project is to:
- We cant to learn and describe basic QA procedures of 7T RF-coils.
- We want to characterize the differences of noise characteristics in fMRI protocols across different coil models; pTx and sTx.
- We want to engage with the community to gather and compare basic QA metrics across scanners.
We hope that these results will be informative as reference data for any 7T sights that are unsure if their SNR is at the optimal level. Furthermore, we hope that findings of this project will pave the way for cross-site large neuroimaging studies
GitHub issue
Project URL
WhoBPyT - Whole-Brain Modelling in PyTorch
EEG
fMRI
nilearn
MNE
machine learning
WhoBPyT - Whole-Brain Modelling in PyTorch
WhoBPyT is a Python library for connectome-based neurophysiological modelling of neuroimaging and other macroscale brain data. At its core is a deep learning-based approach for model fitting and parameter estimation, that capitalizes on the in-built algorithmic differentiation and optimization functionality of PyTorch.
The current WhoBPyT code base is a consolidation of several projects that have used this computational technique to study mechanisms underlying brain dynamics in TMS-EEG, stereotactic EEG, resting-state fMRI.
We have completed a major refactor of the code base that generalizes several key functionalities and improves overall readability. The goal of this OHBM BrainHack project is to improve the first-time user experience with WhoBPyT, principally through docs and tutorial examples on computational modeling of EEG and fMRI data.
GitHub issue
Project URL

Bayesian modelling in perception and action - moving towards sense of agency
Bayesian
Bayesian modelling in perception and action - moving towards sense of agency
In this project, we aim to expand on current trends within Bayesian modeling of perception and action. Our goal is to use computational models to investigate classic theories of sense of agency. Using various open-source tools (e.g. BCI Toolbox, see https://github.com/evans1112/bcitoolbox), we will build a model that allows testing of many assumptions that underly classical and contemporary studies of sense of agency. The structure will be accessible and modular, to allow others to test their questions of interest.
GitHub issue
Project URL
Understanding fMRI through programming
fMRI
documentation
preprocessing
Understanding fMRI through programming
The aim of this project is to crate educational simulations for understanding the functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) signal. We are going to create single script simulations with simple graphical user interfaces to allow self driven exploration of fundamental fMRI concepts such as magnitude, phase, T2* decay, blood oxygenation effect (BOLD), and vascular magnetic field effects. Historically critical papers, equations, and figures will be linked to these scripts to build them as entry point pedagogical devices for people who have programming experience. The long term goal of is to build this repository as an educational resource to teach MRI basics to create other teaching material such as videos. An important source of inspiration for this project is https://www.youtube.com/c/3blue1brown . Two prototypical scripts are used in the videos below which were part of a presentation that required visual beyond still figures or animations:
- [Timestamp 32:35] https://youtu.be/CeDf9YpMtLk?si=I2Ye9Btwr0Y0R1JX&t=1955
- [Timestamp 43:27] https://youtu.be/CeDf9YpMtLk?si=a1ofbstzWPTBwRbA&t=2607
GitHub issue
Project URL

HALFpipe: Advancing reproducible fMRI analysis based on fMRIPrep
BIDS
fMRI
Nipype
preprocessing
HALFpipe: Advancing reproducible fMRI analysis based on fMRIPrep
Using standardized pipelines leads to consistent results, right? We ran fMRIPrep 20.2.7 one hundred times and then calculated functional connectivity matrices using HALFpipe.
- We did this in a multiverse approach where we varied which denoising strategy was applied before connectivity matrix calculation. An interesting next step here is to figure out how to quantify the variability in these matrices depending on the strategy. Are there any strategies that better than others? Any interested contributors may download the data and attempt to answer this question with us!
- We would like to repeat this procedure with newer versions of fMRIPrep, and compare to the baseline that we already ran. How does the variability between versions compare to the variability within a single version? This will require some programming to load in derivatives files from different versions of fMRIPrep and then apply the Nipype workflows from HALFpipe to them. We are welcoming contributors willing to expand their familiarity with Nipype workflows in Python or BIDS derivatives.
- The Enhancing Neuro Imaging Genetics through Meta Analysis (ENIGMA) Consortium conducts the largest brain imaging studies in the world, involving over 500 institutions in 45 countries worldwide. At this time, the ENIGMA Consortium has processed more than fifty thousand fMRI scans using fMRIPrep, mostly using HALFpipe as a user interface to fMRIPrep for ease of use. HALFpipe also calculates downstream results such as functional connectivity maps and matrices. While fMRIPrep supports resampling fMRI data to the cortical surface, the current HALFpipe workflows currently can not use those outputs. We would like to change this, and have a roadmap of the Nipype workflows in HALFpipe that need to be adapted. We would love to discuss the best approaches and potentially even try implementing some of the changes.
GitHub issue
Project URL
PhysioQC: A physiological data Quality Control toolbox with physiopy
git
quality control
PhysioQC: A physiological data Quality Control toolbox with physiopy
Physiopy is a community formed around developing solutions to operate physiological files in neuroimaging setups. The objective of this project is to get a good workflow and command line interface that generates quality analysis metrics and outputs these elements as .csv, .json files, and creates an html visual report. We additionally hope to build useful, interactive widgets and interfaces to help physio users to check and analyze their data with ease.
All contributions are welcome and accepted, from any level of contribution. We follow the all-contributors specification to report contributions, and adopt physiopy’s contributors guide and code of conduct.
GitHub issue
Project URL

Neurosynth Compose: Ecosystem for Reproducible Meta-Analyses
cognition
fMRI
LLM
documentation
statistics
Neurosynth Compose: Ecosystem for Reproducible Meta-Analyses
We are aiming to make meta-analyses more systematic, reproducible, and overall less painful with an online interface and lots of pre-ingested data for you to use freely!
Our platform now hosts over 30,000 neuroimaging papers that report coordinates, making the arduous phase of transcribing coordinates simpler than ever.
We have a number of projects to work on, whether it’s your first time programming or if you’re a seasoned veteran.
Novice
- Test out our sleuth file import feature (try to break it and give feedback)
- Work on a script to add DOI/PMID to the sleuth files automatically
- Use our tutorial and give feedback
- Help validate paper-extracted information from GPT
Intermediate
- write code to create figures to do some exploratory data analysis/Validation on data we’ve ingested.
- formalize the DOI/PMID adding script into a function in NiMARE
- profile memory consumption in running the NiMARE reports CBMA module
- add documentation to publang: interface to extract information from academic papers (https://github.com/adelavega/publang)
Advanced
- redo the cognitive atlas python package using a more modern API generator
- help create a script to extract references to papers within meta-analysis papers
- create a NIDM to NiMARE function
- Prompt Engineering/workflow design for publang to extract task information
- representing participant demographics in our database.
GitHub issue
Project URL

Injecting BIDS schema into bids2table
BIDS
fMRI
Injecting BIDS schema into bids2table
bids2table is a BIDS indexing and query tool written in Python. It is orders of magnitude faster than PyBIDS. We did not write this, but we want to use it. Before committing to this, it would be good to make sure it’s extensible as BIDS grows by building components from the BIDS schema.
We’ll look into how it’s written now, and see what we can do, ideally without making it slower.
GitHub issue
Project URL

ChRIS-cljs
Containers
ChRIS-cljs
ChRIS is a container scheduling platform for neuroscience, consisting of a core backend, a set of container scheduling microservices, interfaces to kubernetes, OpenShift, slurm, and others.. It has a rich and expressive REST API, as well as a JavaScript GUI, a javascript library and a python library. The purpose of this hack is to (start to) build a nodejs CLI using the js library to provide a REPL “shell” for ChRIS.
GitHub issue
Project URL